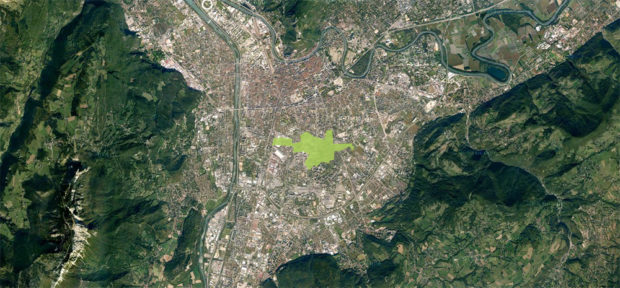
A few months ago we ended one of the longest, intense and complex projects our office Ecosistema Urbano has done so far, the Masterplan of the Historic Downtown of Asunción, awarded in an international competition and developed with a multidisciplinary team between Madrid and the Mother of Cities, Asunción.
art
October 4, 2016
September 30, 2016

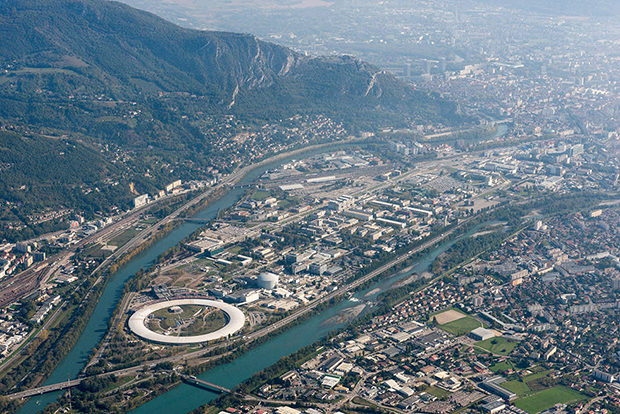
Nous sommes heureux de vous annoncer que nous venons d’être sélectionnés pour le projet d’aménagement de la ZAC Flaubert à Grenoble, une grande et excitante aventure de renouvellement urbain au coeur même de la métropole grenobloise. C´est le résultat de notre collaboration avec Sathy, TN Plus, OGI (ingénierie), Res Publica, et VPEAS.
Il s’agit d’un projet de renouvellement urbain sur un territoire jusqu’alors peu valorisé. La ZAC Flaubert est une zone de transition entre Nord et Sud et entre Est et Ouest de la ville, elle est traversée par de grands axes de circulations qui font de cette ZAC un espace au développement très stratégique. Dû à sa très grande surface (90 hectares) ce projet de grande envergure soulève de multiples enjeux pour la ville et ses habitants. Comment donner une identité à cette zone qui n’est actuellement qu’un assemblage artificiel de micro-identités de quartier ?
Le nouveau maire écologiste désire mettre tout en oeuvre pour intégrer les citoyens à la co-construction de cette zone et plus largement à leur ville. Pour ce projet, il a fait l’engagement de ne jamais cesser le dialogue avec les habitants, les riverains et les commerçants au cours de chacune des phases du projet. Il est également question d’élargir le panel à de nombreux acteurs économiques, institutionnels, académiques de Grenoble grâce à des débats et des discussions. L’objectif est d´échanger les points de vues et les différents avis sur l´avenir de Flaubert.
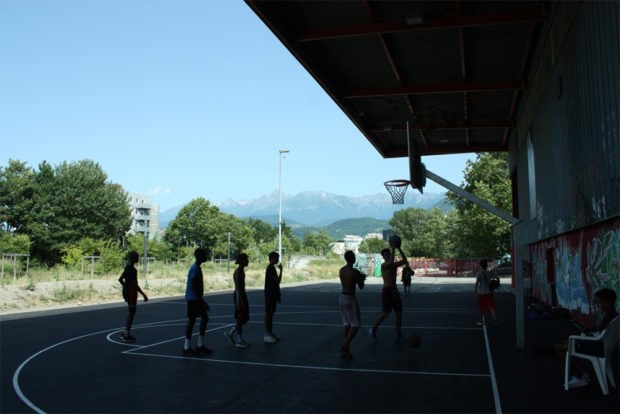
En juin dernier, lors de notre première visite, nous avons pu mieux comprendre les enjeux du territoire et observer de près la vie urbaine.
Notre objectif actuel est d´étudier en profondeur le projet, pour comprendre à quel point il est complexe et pour nous rendre compte des challenges qui nous attendent.
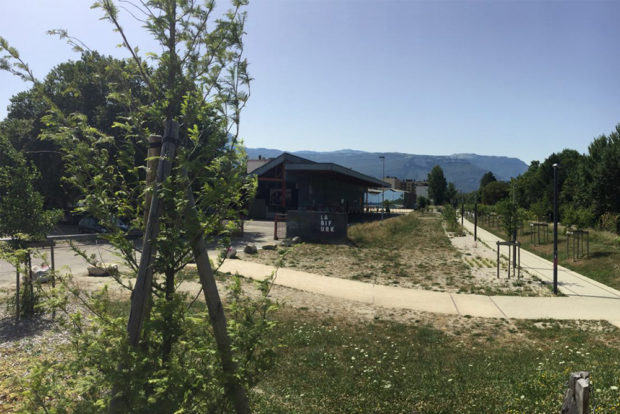
Un des moments fort de cette visite fût la découverte de la “Bifurk“ et de son “éco-système”, c’est un espace hybride où la vie bat son plein grâce à l’équipe et à de nombreuses associations très actives, qui ont su transformer cet ancien entrepôt industriel en un espace polymorphe où l´on peut trouver une grande diversité d’activités : théâtre, concerts, expositions et même un skatepark. Juste à côté, “La Plage” est la première plage urbaine permanente construite en France. Dédiée à la pratique de sport de sable elle offre au Grenoblois un large choix de sports des plus conventionnels aux plus insolites.
En face de ces lieux emblématiques de la ZAC, il est question d’implanter la casa “Terra Nostra”, une maison en terre et bois construite par les étudiants des écoles d’architecture de Lyon et Grenoble. C’est une occasion de connecter au projet une infrastructure existante, en créant une espace dédié à l´urbanisation de Flaubert à l´intérieur de la maison.
La force de Grenoble est son ouverture d’esprit avant-gardiste : innovante et créative, elle s’inscrit depuis deux décennies dans un programme promouvant une ville plus agréable, plus sociale, plus durable. À l’écoute de ses citoyens et à l’affût des innovations techniques, technologiques, sociales et économique, Grenoble est bien plus que la 11 ème métropole française. Elle est un exemple novateur d’une volonté politique et citoyenne visant à construire autrement la ville de demain. Plusieurs initiatives urbaines et citoyennes singulières ont profondément participé à la mutation de la ville et à sa nouvelle morphologie. Le changement passe par de “grandes actions” mais aussi par de “petites initiatives” qui accumulées donne à la ville une identité propre. La ville soutient chaque année plus de 600 actions qui se regroupent autour de trois grandes lignes directrices : favoriser la participation des habitants, lutter contre toute forme d’inégalités sociales, mettre en avant des territoires les plus fragilisés.
La forte volonté de faire participer les citoyens au renouvellement de Flaubert se place dans la continuité d’une politique ouverte aux propositions de chacun et à l’écoute de ses citoyens. L´intégration de chaque partie prenante au projet permet de recentrer la ville sur ses usagers, de se focaliser sur la ville “à taille humaine”, faite avant tout pour ses habitants. Ce nouveau regard sur la ville et la re-qualification du cadre de vie qu’il engendre participe fortement à l’attractivité territoriale de Grenoble, souvent surnommée la “Capitale des Alpes”. Grenoble est un véritable laboratoire urbain : en 2005, le conseil a adopté un programme de rénovation urbaine soutenant les opérations de renouvellement urbains au sein de la ville en leur accordant un budget très conséquent. Illustrons cette singularité :
Une ville qui réinvente son architecture
La construction d’un des premiers éco-quartiers français dans l’ancienne caserne militaire de Bonne en plein centre ville ( 5 hectares) est un exemple qui concrétise le désir de concilier ville et environnement. Loisos Sava, architecte en chef du projet prône la réinvention de la façon de construire, offrant à la fois une baisse des dépenses énergétiques, une mixité sociale et une mixité fonctionnelle. Cet éco-quartier de nombreuses fois primé a notamment reçu en 2009 le Grand prix national “Ecoquartier” délivré par le ministère de l’Ecologie, de l’Energie, du Développement durable et de la Mer. De plus, très récemment une vaste opération de révision du Plan Local d’Urbanisme intercommunal (PLUi) en 2015 a été opéré. Une des mesures phares de cette révision est la diminution de la hauteur maximale de construction.
Une ville accessible et durable
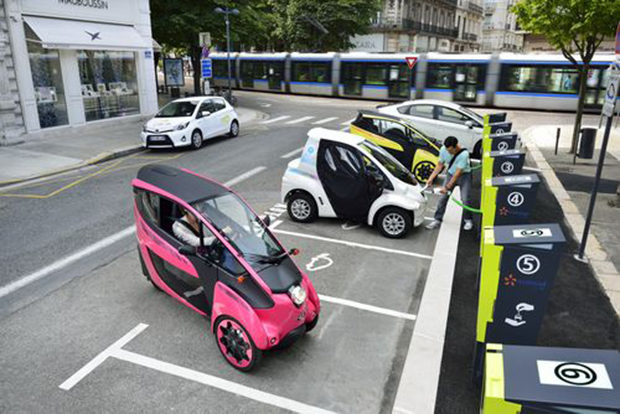
Grenoble est également une ville pour tous, mettant au centre de ses préocupations l’accueil de tous les publics. En effet elle a été classée première ville de France sur le baromètre de l’accessibilité aux handicaps avec une moyenne de 18,7 et deuxième ville européenne. Grenoble a créé un service d’auto-partage de véhicules électriques appelé “CitéLib” en collaboration avec Toyota qui souhaitait tester ici-même ce système de location unique au monde. Le but est de stimuler la multi-modalité de la ville, en effet ces véhicules 100% électriques servent à incrémenter l’offre de transports publics existants en proposant une solution alternative pour les “premiers et derniers kilomètres”.
Une ville qui s’engage
De plus, Grenoble a su marquer les esprits par une prise de position très forte en 2015. En effet, c’est la première ville européenne à bannir les publicités de ses rues, proposition qui a été soutenu par leur nouveau maire écologiste. La lutte contre la “pollution visuelle” prive la ville d’une manne de revenus importante. Des affichages dédiés aux activités culturelles et aux informations de la mairie remplacent les affichages actuels. De nombreuses autres villes voient en Grenoble un modèle à suivre.
Une ville innovante
Que ce soit au niveau national, européen ou international, Grenoble se démarque par son goût pour l’innovation. En effet Grenoble a reçu de nombreux prix et certifications à toutes les échelles:
National
En 2014, Grenoble a été labellisée “FrenchTech” ainsi que huit autres villes de l’hexagone. Ce label a pour but de donner une meilleure visibilité à l’international de l’attractivité technologique des villes françaises.
Européen
Grenoble a été, en 2014, sacrée deuxième ville la plus innovante d’Europe après Barcelone au concours pour le prix de la première capitale européenne de l’innovation. Ce prix vise à récompenser la ville qui offre le meilleur «écosystème d’innovation» en connectant les citoyens, les organismes publics, les établissements d’enseignement et les entreprises.
Mondial
Cette «iCapitale» a également été cité parmi les 15 villes les plus innovantes par le magazine Forbes en 2013.
Le quartier de la Presqu’île, au Nord de la ville est spécialisé dans les technologies de pointe. Cette Silicon Valley grenobloise est un véritable pôle d’attraction pour le reste de la ville et participe considérablement à sa renommée. La connexion du quartier de la presqu’île à la ZAC Flaubert constituerait une formidable opportunité pour le quartier objet de notre projet qui pourrait donc créer en son sein de nouvelles dynamiques. Ce n’est qu’une des propositions parmi tant d’autres, aucune piste n’est écartée, l’idée étant de procéder par étapes et de se donner un temps d’expérimentation afin d’envisager plusieurs hypothèses éventuelles.
Pour conclure, autant dire qu’en de nombreux points Grenoble sait se renouveler et imposer une nouvelle façon de penser la ville. Ces exemples inspirants et stimulants placent la barre très haut, le défi est grand et nous sommes honorés d’avoir l’opportunité de participer à l’élaboration de ce laboratoire urbain qu’est la ville de Grenoble.

À bientôt pour plus de nouvelles sur ce projet !
October 21, 2013
A pocos pasos de la estación de metro de Bethnal Green está la primera sede del Victoria & Albert Museum que hoy alberga el mismo museo dedicado a la infancia: ¡el Museum of Childhood!
October 7, 2013
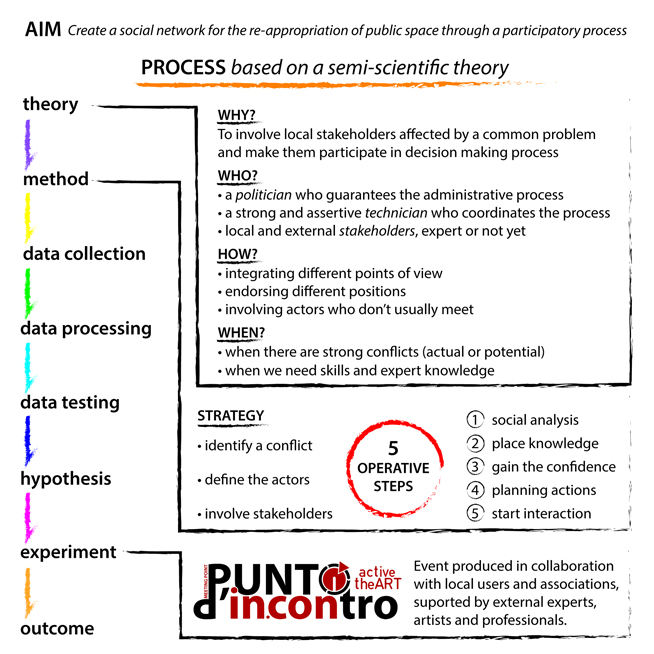
In order to achieve the Post-Master called Urban Research Lab Sardinia – Environmental Design at the Università di Sassari (DAP), in partnership with the Dessau Institute of Architecture (DIA) of Anhalt University of Applied Sciences, an article will be published about the project made during the italian period, under the supervision of Ecosistema Urbano: Punto d’incontro.
This is an excerpt of the introduction, including some references and case studies.
The role of the architect
The role of the architect has always been, throughout ancient and modern history, a reference point for the city growth and development. Nowadays, this figure is undergoing a massive transformation, which cannot ignore social aspects. The modern architect helps to integrate production processes within the spaces users live and use in everyday life.
The article aims to present an experiment that was personally led in a very specific local community in Sardinia (Italy) which is affected by logistic, economical and management problems. Through theoretical studies and personal analysis of a variety of existing projects, a detailed process was drafted in order to suggest a strategic action plan.
Western society has scarce resources and the European architect often asks the following question, what can I do now without nothing? In this hard times, it is far more difficult for closed solution to be imposed by a power minority than for specific temporary actions to be applied based on grassroots talks, because sensitivity is high and social groups are highly resistant to accepting any changes which have not come from within their ranks. Ecosistema Urbano (2011). “Negotiating at all level”. A + T 38. 120
Strategy & Tactics
The first input to the change came with the drafting of Agenda 21, a voluntarily implemented action plan of the United Nations with regard to sustainable development. It emphasises that broad public participation in decision making is a fundamental prerequisite for achieving sustainable development. The main goal is trying to involve the local communities in the construction process of the future of the cities. When public space is concerned, there are two ways to run over: strategy and tactics. Both are tools of equal value, but with different typology of method; they are usually known as top-down or bottom-up processes.
Tactics are actions which take place on enemy territory while strategy is always enacted on home ground. Which can lead to an immediate run-of-the-mill sharing out of roles: strategy is an instrument of power, tactics are used by citizens; strategy occupies space, tactics play out in time; strategy is used to control, tactics to protest. De Certeau, M.(1988). The Practice of Everyday Life. University of California Press
Recent developments of these concepts became well known under different name, but in essence they are all the same.
Tactical urbanism. It is defined as small-scale improvements in an effort to effect large-scale, long-term change.
Placemaking. It is the act of enlivening public spaces and places for the betterment of the community and its neighbors.
Participatory design. It is an approach to the assessment, design, and development of technological and organizational systems that places a premium on the active involvement of workplace practitioners (usually potential or current users of the system).
The following scheme represents the stages of the experiment:
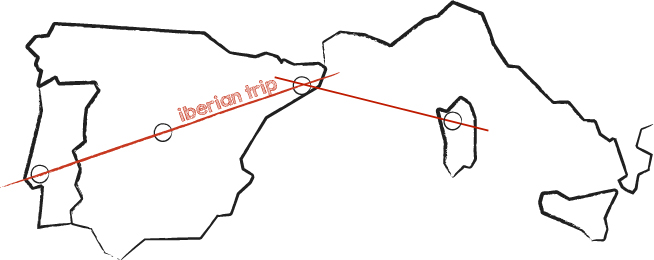
The Iberian trip
There was the necessity to analyze the theory, exploring some case studies and finding some references. This processes are already very disseminated all over the world, especially in USA and north Europe, where the citizens have a great sense of community and cooperation.
Nevertheless this research focused on the Mediterranean area, in this particular case in the Iberian peninsula, where the lack of organization meets high quality and creativity, typical of the Latin culture. Some of the cases shown here are real established structures, others are spaces under construction and constantly changing. The connecting link is always one of active participation.
LXFACTORY – Lisbon
An urban fragment, kept hidden for years, is now returned to the city in the form of LXFactory. A creative island occupied by corporations and professionals of the industry serves also has stage for a diverse set of happenings related to fashion, publicity, communication, fine arts, architecture, music, etc.
El campo de cebada – Madrid
A group of neighbours called Distrito Centro promoted a temporary use of the vacant lof of a former public pool demolished in a district of Madrid, during the time in which the work planned for urban reuse was not to be carried out. The intention is that the space will accommodate all types of proposals/activities/projects (cultural, social, artistic, sport) for the use and enjoyment of the people of the district and all the city.
Matadero – Madrid
The old slaughterhouse and livestock market, where Matadero Madrid is now located, was built according with the project of the architect Luis Bellido. The site was architecturally transformed.
Matadero Madrid’s mission is to promote creation in all its forms and expressions. With special attention to cross-sectorial propositions, it focuses on three main action areas: training, production and dissemination.
Fabra i Coats Creation Factory – Barcelona
Fabra i Coats is a multidisciplinary space which will be promoting artistic hybridisation to become a point of reference in artistic research and in the generation of new quality contents, as well as a meeting point for groups, creators and proposals from different spheres and backgrounds.
The goal is to give support to artistic creation and it has workspaces for the performing arts, music, plastic and visual arts, multimedia creation and also for projects related to information and communication technology.

Sometimes these kind of actions are not supported by a physical space, but by the people that build their spaces through some collective iniziatives, occasionally supported by a politician organization or made by self-funded artistic groups.
Urbact
It is a European exchange and learning programme promoting sustainable urban development. They enable cities to work together to develop solutions to major urban challenges, reaffirming the key role they play in facing increasingly complex societal changes. URBACT spans over 500 cities, 29 countries and 7,000 active participants.
Collectif ETC
Born in Strasbourg in 2009, this collective gathered energy around a common dynamic questioning of urban space. Through different means and different skills it wants to be a medium for experimentation. They believe that the different users of the city (residents and professionals) can all be involved in its development to a wide range of scales. The purpose and importance of these urban experiments is not only the result but also the process that generates it, as well as the new environment and new behavior it generates.
Boa Mistura
It is an urban art group formed at the end of 2001 in Madrid, Spain. Its members have diversity of perspectives, distinct visions which complement each other, and combine to create something unique and coherent.
Madrid Street Art Project
It is a noprofit association that through the organization of various activities and initiatives (urban Safaris, workshops, lectures, recovery rooms) aims to contribute to these reflections, to encourage citizens to enjoy urban art, contribute to its dissemination and support its creators.
Conclusions
The final article will aim to give some semi-scientific guidelines to build participatory and inclusive societies. The new frontier of the architect should be to drive local communities in the management of public and private space, involving them in the construction process of the urban renewal. This is when the architect, as a highly knowledgeable technician, plays an essential role to mend the relation between politicians and common people.
September 30, 2013
Hoy comparto con ustedes un proyecto un poco especial descubierto mientras estaba buscando información sobre el festival Burning Man y educación: les presento el Youth Educational Spacecraft project (Y.E.S.). Se trata de un aula móvil con forma de nave espacial diseñada y construida por un grupo de artistas, ingenieros, niños y voluntarios. En el origen del proyecto encontramos a los artistas y educadores Dana Albany y Kal Spelletich.
En este espacio los niños podrán disfrutar de diferentes talleres como: grabación y edición de vídeo, fabricación de moldes, fusión y soplado de vidrio para los portales exteriores e interiores, mosaicos, robótica (vehículo lunar, el brazo tele-robótico), la electrónica, la construcción de instalaciones, carpintería, jardinería, cableado eléctrico, reparación de objetos, purificación del agua, vigilancia por vídeo, interfaces electrónicas, alternativas de cocina, la energía solar, la iluminación, sistemas de control remoto, historia del arte, promover y exhibir su arte. Para esto, la nave está equipada con unos “elementos robóticos de sorpresa”; generador de luz con manivela, un robot para tocar violín, etc.
Aquí, el proceso educativo de una obra en común permite despertar la curiosidad de los niños. Los expertos usan recursos técnicos específicos, digitales o analógicos, que controlan perfectamente y transmiten un conocimiento con la práctica.
El proyecto arrancó en el Exploratorium de San Francisco y siguió con Burning Man 2013. La movilidad de esta micro-arquitectura les permite aumentar su red de participantes. Su objetivo es trabajar con escuelas, centros artísticos, científicos, festivales o cualquier otra estructura que defienda la creatividad.
Ver más:
– Walker with hat and glass
– Spaceship design
– Dana Albany explaining de spaceship concept
– YES at Bruning Man 2013Financiación actual: Maker Faire, Black Rock Arts Foundation, The Exploratorium, Black Rock City LLC, Burning Man Project, The Crucible y un business angel.
March 13, 2011
Today I present another project by Candy Chang. An interesting installation on a side of an abandoned house in her neighborhood in New Orleans. She transformed it into a giant chalkboard where residents could fill in the blank and remember what is important to them in life. The project is also about turning a neglected space into a constructive one where we can learn the hopes and aspirations of the people around us. continue reading
March 3, 2011

Os presento el proyecto I Wish This Was…de la artista Candy Chang que se autodefine como ‘public installation artist, designer, urban planner, and co-founder of Civic Center who likes to make cities more comfortable for people‘.
Este es un proyecto que lleva a cabo en su barrio de Nueva Orleans, donde mediante el diseño de unas sencillas pegatinas crea un elemento de comunicación para que los vecinos expresen sus deseos en los edificios y solares vacíos o abandonados (una especie de what if .. analógico) sigue leyendo
February 18, 2009

FAVELA PAINTING IS A PROJECT BY THE FIRMEZA FOUNDATION
The Firmeza Foundation creates striking artworks in places where people are being socially excluded. The foundation collaborates with local people to use art to combat prejuducie, create sustainable solutions, and attract the world’s attention. continue reading
February 2, 2009
LONDON CALLING
Category: ⚐ EN+architecture+art+sustainability+Uncategorized
“Scientists think that ice will probably disappear from the North Pole for the first time by this summer 2008 due to the global warming. We would like to express our solidarity with the hungry – and probably angry – polar bears that will soon reach our lands (?) trying to find some dry land and food. What about architecture?”