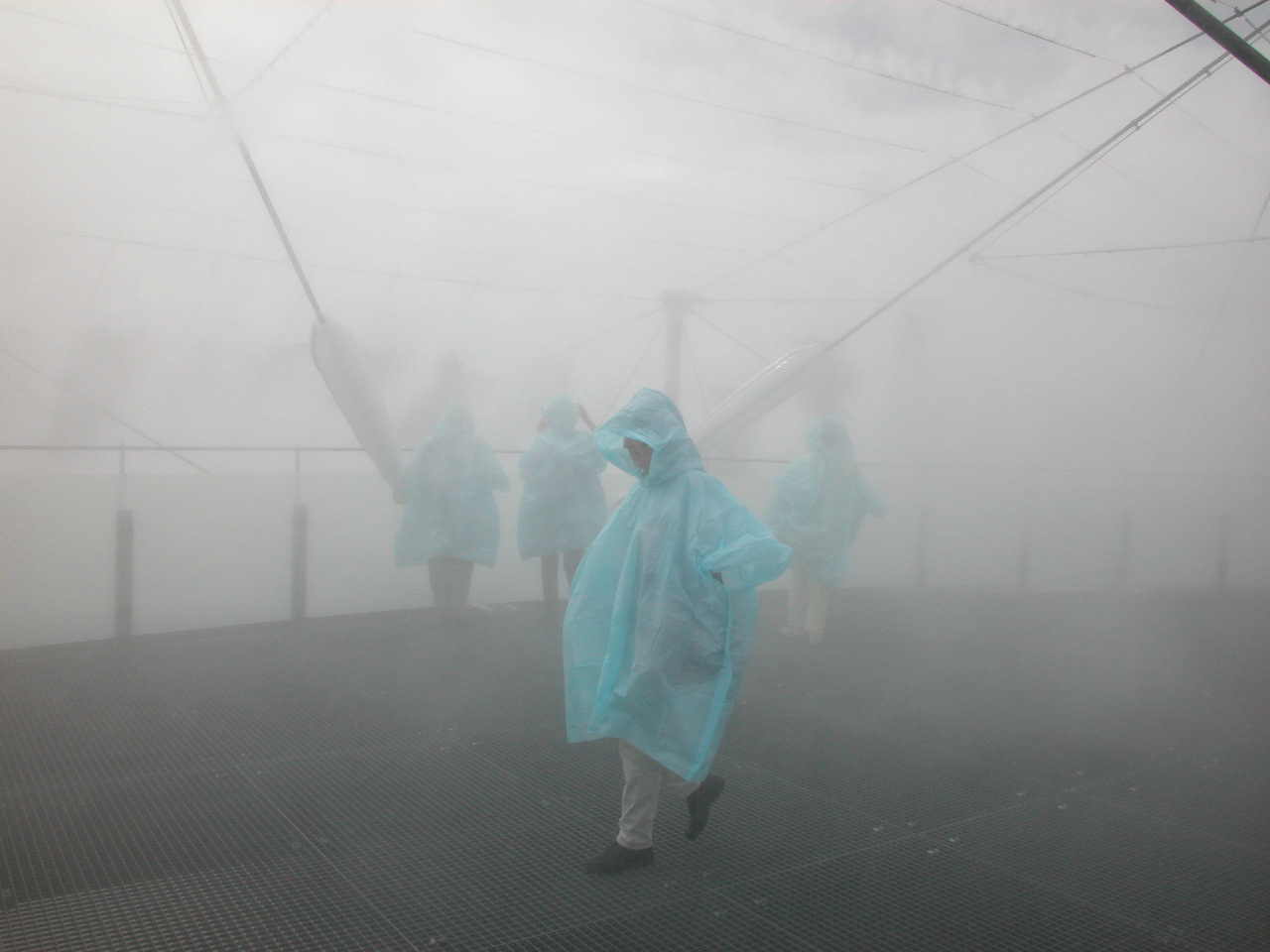
Digestible Gulf Stream, Philippe Rahm, Venice Biennale 2008. Image courtesy of Philippe Rahm.
Con·vec·tion. Convection results from the tendency of most fluids to expand when heated.
The use of convective air flows with the purpose of cooling traditional houses was not alien to traditional Persian and middle eastern architecture. Joining the “simple” badgir ventilation system with more refined and complex cooling technologies was one of the most advanced points reached by Persian/Iranian building knowledge. Passive cooling systems in the Yazd desert were so advanced that iced formed (and accumulated) during the cold winters could be conserved frozen until the height of the long, hot, desertic summer.
In addition to sensible cooling, the cooling caused by a change of air temperature but not its humidity, badgir combined with a savvy use of water can provide also evaporative cooling which is generally more effective than sensible cooling alone.

Water deposit cooled with badgirs in the Yazd desert, in Iran. Image courtesy of Flickr user dynamosquito, CC BY-SA
In order to do so, windcatchers have to work together with a water source that supplies water which is then evaporated cooling down the flowing air, this can be achieved in many ways. The first one is taking advantage of the of the basement damp walls of the windcacher itself, if there is enough humidity in the underground the basement walls will be constantly wet and when the wind tower is working as an air intake the evaporation of the thin superficial layer of water will cool down the downward incoming stream of air. The second solution is to put a water source, if available, right under the shaft of the tower, a fountain or a small pool is used in this case, sensibly and evaporatively cooling down the entering wind. A great example, found in Yazd, combines and refines even more these two methods placing the tower further than usual from the house (50 m) and then using an underground tunnel to connect the tower with the house. The tunnel, being underground benefits both from the earth thermal inertia and from the humidity of the soil and at the end of the tunnel a fountain is placed to cool down even more the air. The third, and more advanced, passive cooling system based on windcatchers benefits from an underground water stream to cool down the water.

Climatic Tree in the Vallecas Ecoboulevard, Madrid 2004. Image courtesy of Ecosistema Urbano.
The use of convection with the purpose of cooling public space is mostly centered on evaporative towers, in a normal evaporative (cooling) tower hot water is distributed in the upper part of the tower, the sprayed hot water release heat in the atmosphere condensing and flowing down to the bottom of the tower where it is collected and recirculated if it’s the case. In evaporative towers designed to cool the surrounding space the process is inverted, cool water is sprayed with nozzles at the top of the tower and rapidly evaporating absorbs energy from the air coming in from the top of the tower, the cooler and more humid air being denser descends to the bottom and causing the area above it to cool down. The design of an evaporative tower able to work properly is challenging, a single design flaw or dysfunction can cause the sprayed water to condensate an drip.
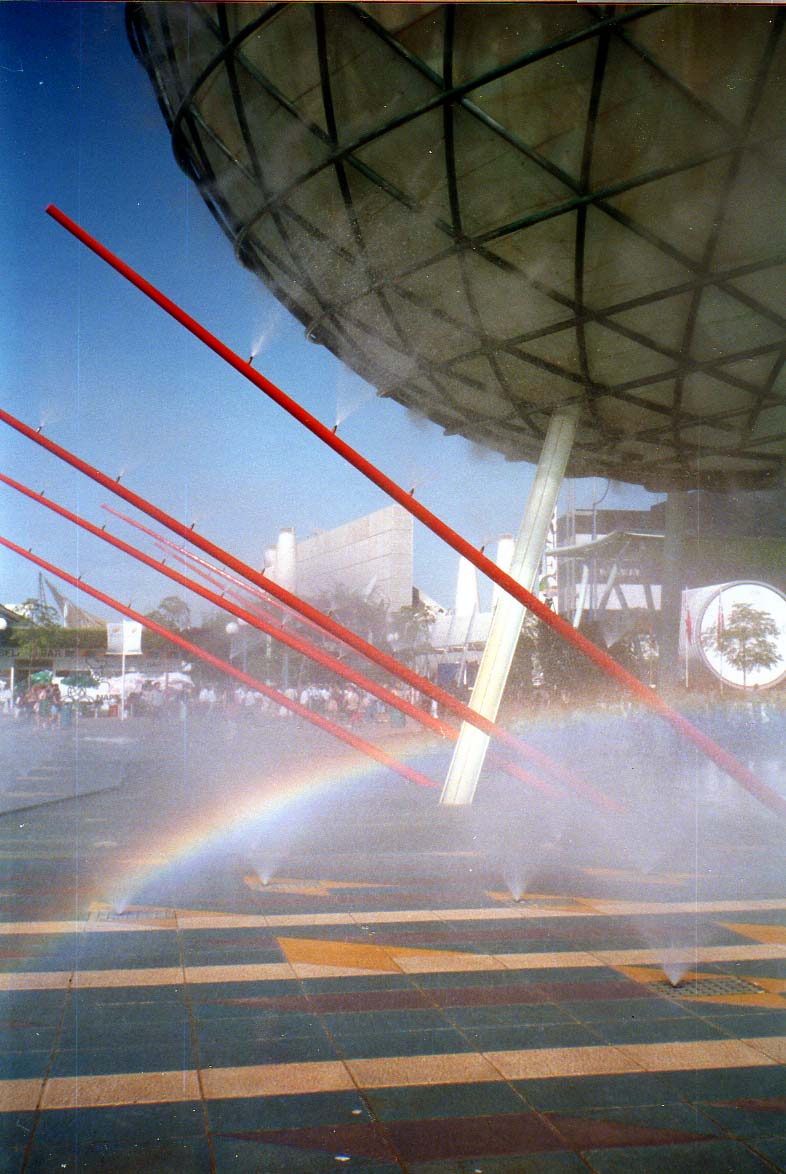
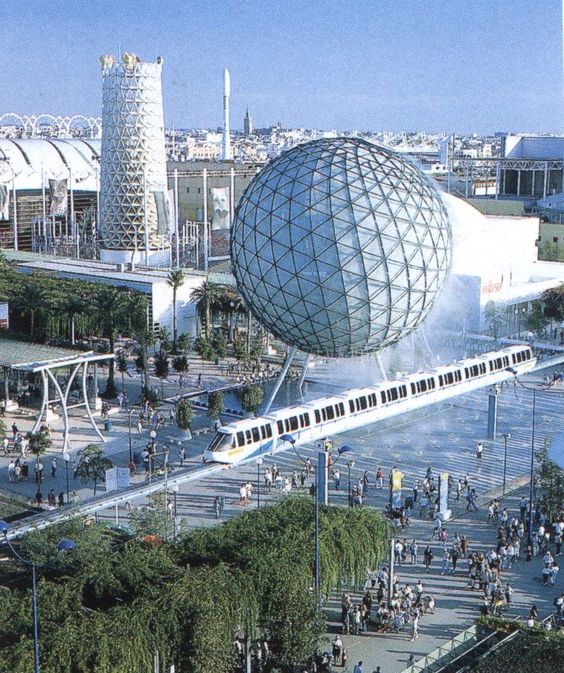
During the 1992 Seville Expo the white towers of the Avenida de Europa were originally designed just to be architectural objects landscaping one of the main avenues of the exhibition but considering a wider plan to improve public space comfort in the whole exhibition area, technically developed with the help of the “termotecnica” group of the university of Seville, were converted into evaporative towers to improve the environmental conditions in the area.
The design, obviously not conceived thinking about the cooling effectiveness, had to be converted a posteriori into a cooling machine. Two main modifications were made: a wind collecting cap was added to the top of the tower and nozzles were installed inside it. For six months the exhibition remained open and the engineers responsible for the bioclimatic design of the event collected data about the functioning and the performances of the design (the report can be found in this book). The added wind-collecting cap proved to be too small for the purpose it was installed and was not sufficient to “catch” enough wind during an average summer day. The second flaw was caused by the structural design of the tower itself, the internal part of the chimney wasn’t smooth and wasn’t totally free either, the secondary steel structure that stiffened the tower was in fact a lattice continuously crossing the chimney section, water nozzles were installed in circles on the inner perimeter of the membrane and functioned properly but the vaporized water copiously condensed on the lattice structure causing continuous dripping under the tower itself. This was obviously a major flaw and the towers functioned only partially, also due to the difficult maintenance of the water nozzles.
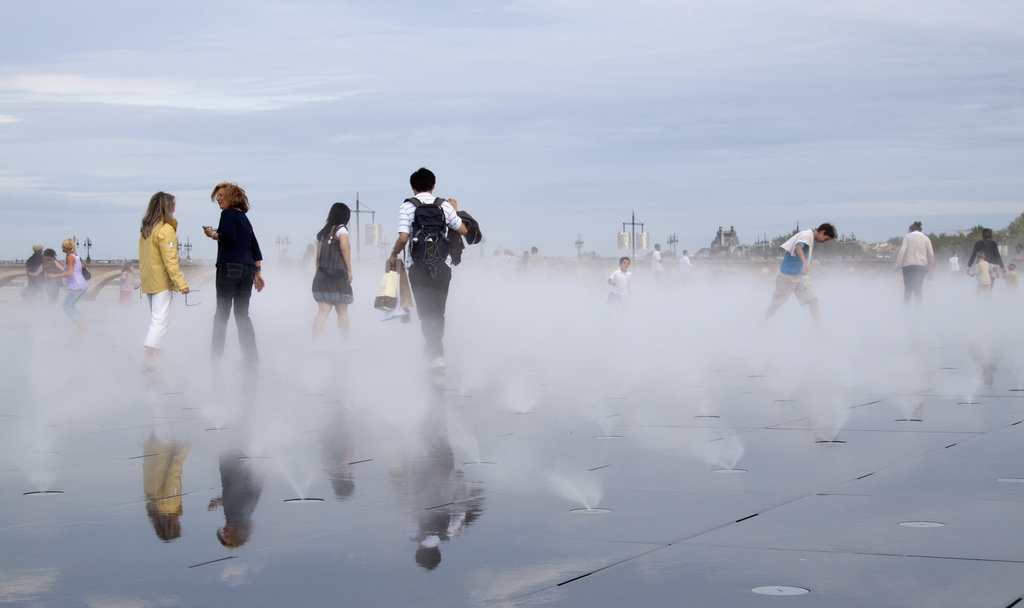
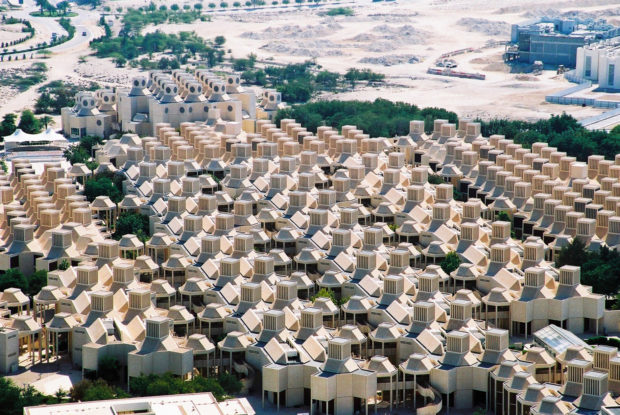
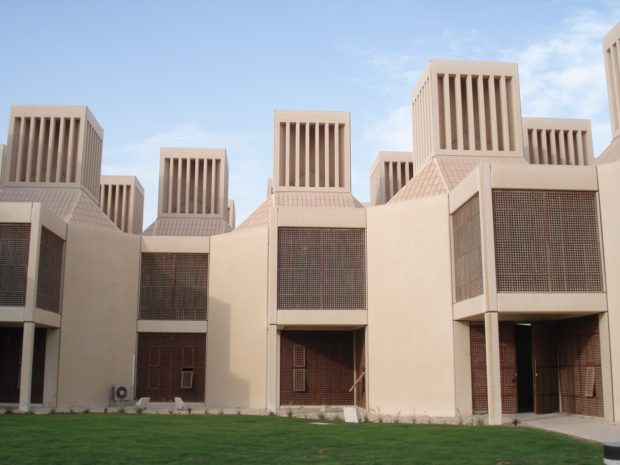
In 2004 Ecosistema Urbano realized one of its most iconic designs, the eco bulevard in Vallecas, Madrid. Each one of the three trees has different characteristics and each one is focused on a different aspect of public space, but in this case the most interesting is the northernmost one that was designed as a rack of twelve evaporative cooling towers grouped to form a semi-enclosed public space shaded and cooled by the bioclimatic tree. Each one of the cylinders is made of two textile tubes, the exterior and reflexive one creates a protective layer for the inner cooling mechanism, the interior tube is the evaporative tower itself. A cap, provided with three openings to collect winds from all directions, is placed on the top of the inner cylinder, right under the cap there is a fan that starts spinning when temperatures rise above 28ºC to increment the existing breeze or to move the air if there is no breeze at all. About at the height of the fan water is sprayed creating a fine mist and its evaporation greatly increases the cooling effect on the air descending in the inner tube and then exiting in the semi-enclosed public space, delimited by the crown of the cooling towers.

Ecobulevar- Arbol de Aire, Ecosistema Urbano, 2004, Ensanche de Vallecas, Madrid.
The ecobulevar, being a fully designed public space, can count on many other design characteristics that improve the overall functioning of the cooling towers, their efficiency and the energetic behavior. The design of the public space under the “tree” is very important, the enclosing section, creates a favorable space for artificial climate conditioning, though it is an open space the “habitable” part (the first 2m from the ground) are somehow closed by the design of the pavement itself, this design contributes to the refrigeration of the central area reducing the hot breeze influence at the ground level and avoiding the direct escape of cooled air. Solar panels contribute to the over sustainability of the artifact generating enough energy to power the fans and the pump for the water. Extensive studies on the ecobulevar, demonstrated that air temperature at the ground level can be up to 9ºC cooler than the air at the top of the tree and that the average temperature difference is around 6,5ºC.
The last two examples are practically based on the same design principle but there are huge differences concerning both the size and the technological character of the project.
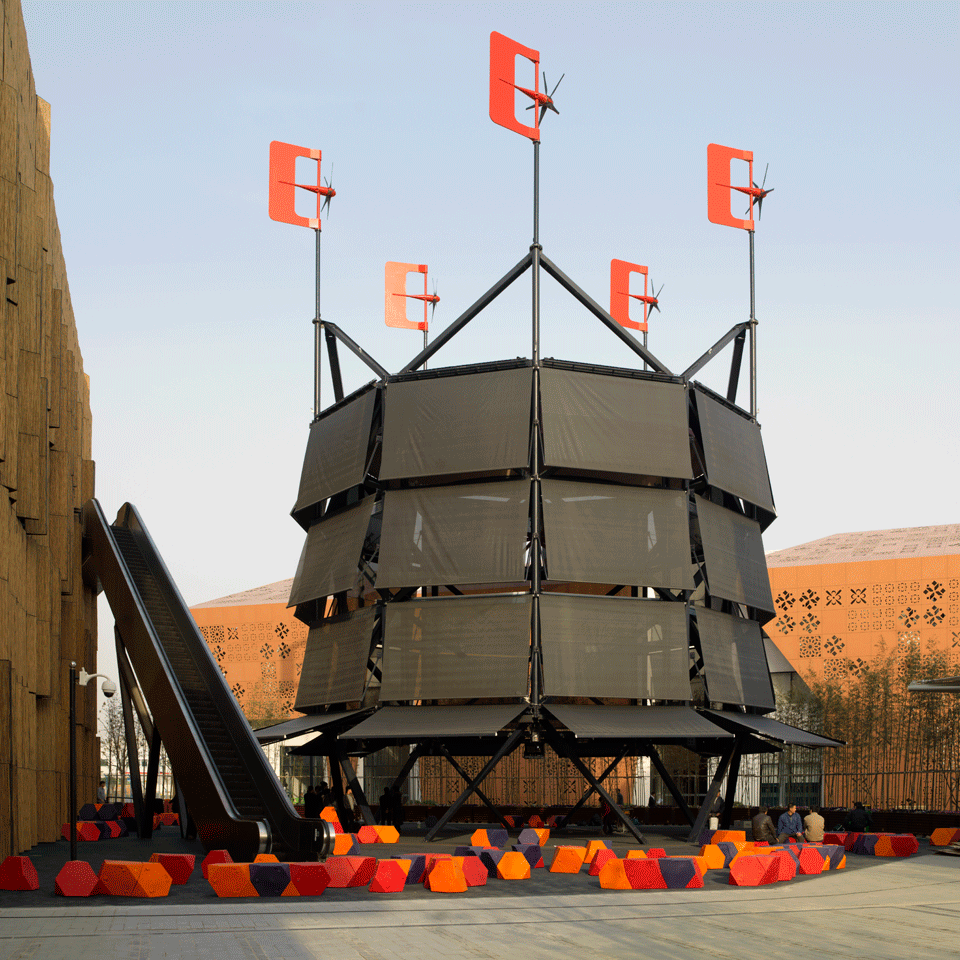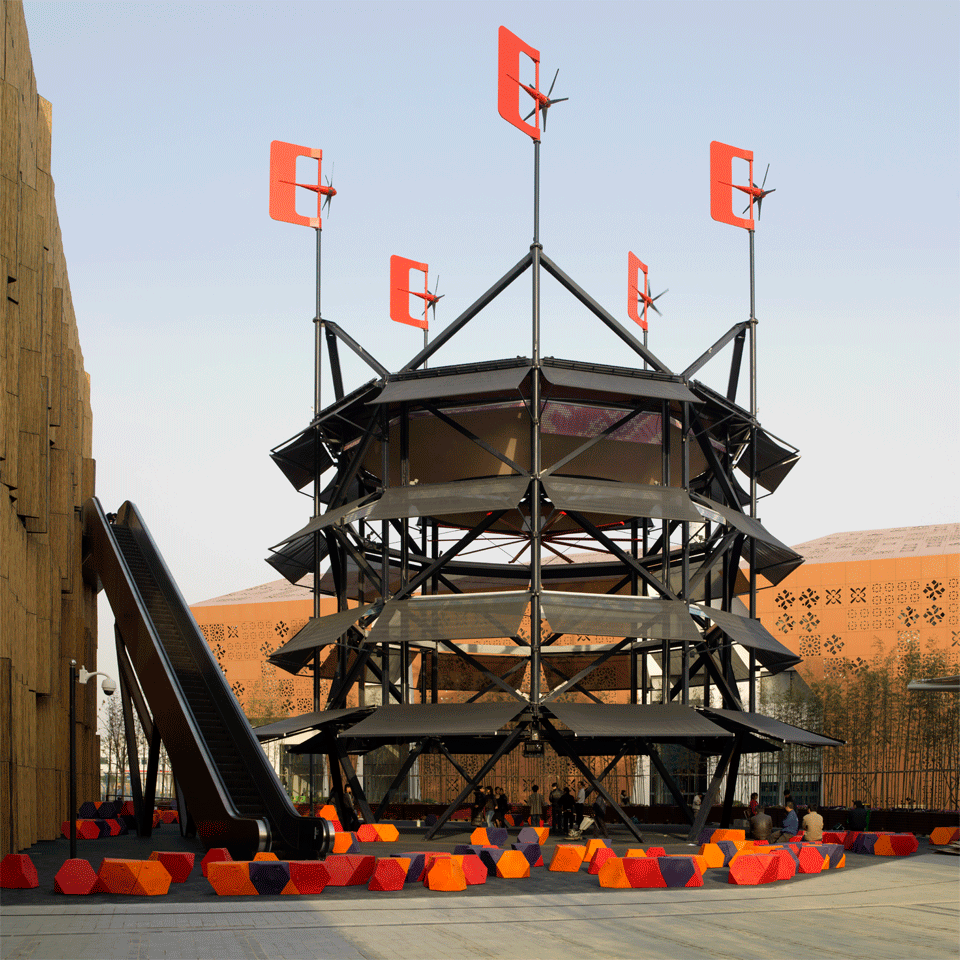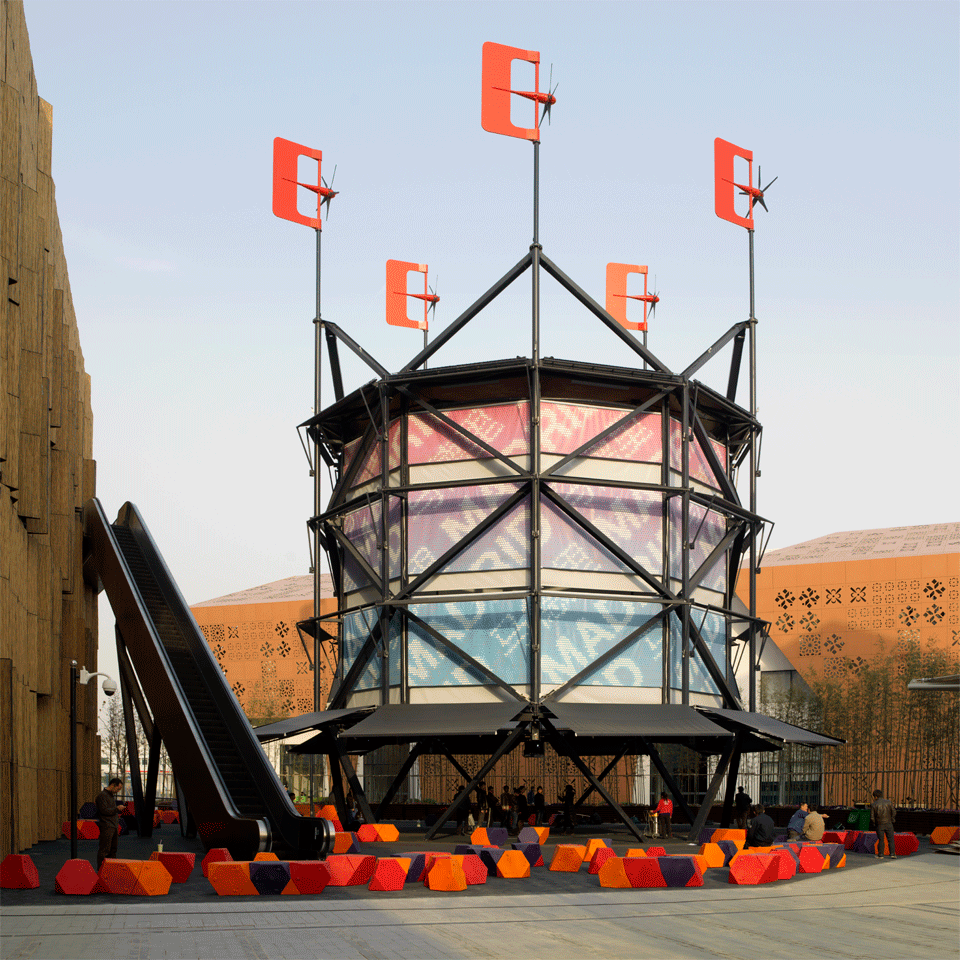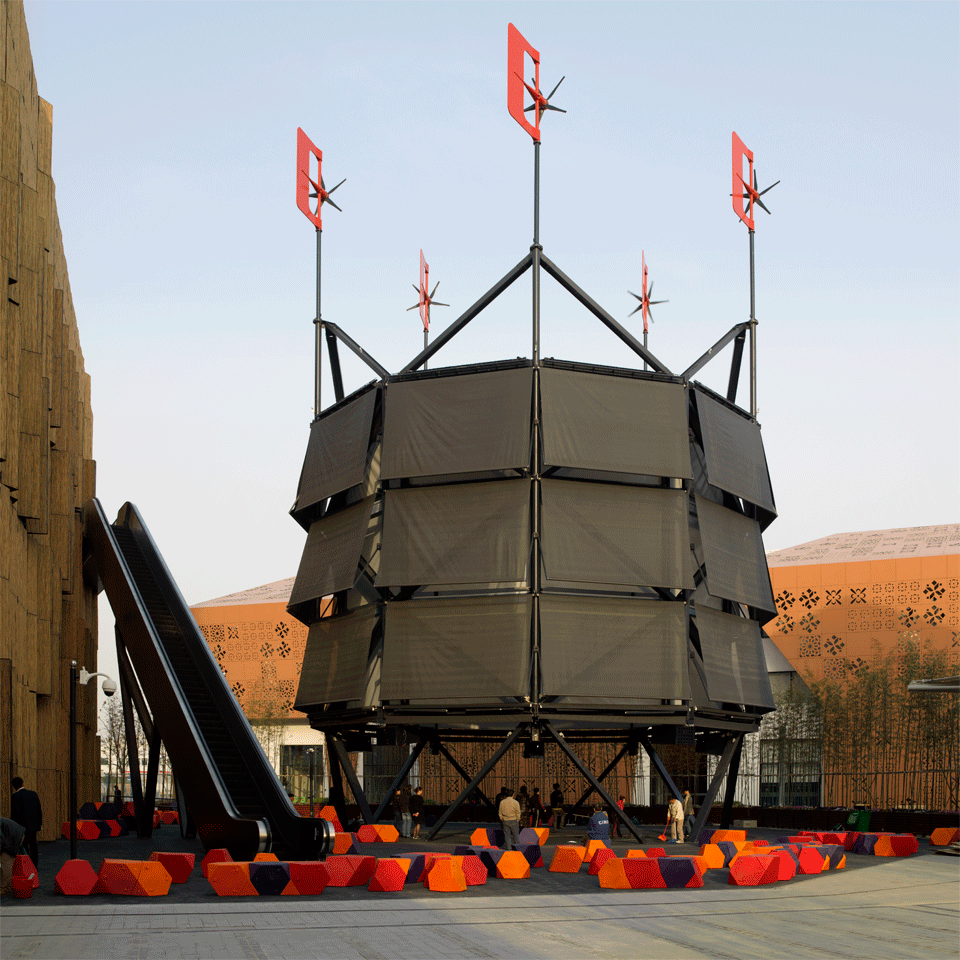
The first one is the wind tower that the British architects Foster+Partners designed for the Masdar Institute in the planned city of Masdar, Abhu Dhabi (which they also planned). The Masdar institute is, as of 2016, one of the few built parts of the city, which, in turn, is facing serious development and financial problems with only the 5% of the planned area being completed. The core plaza of the institute hosts a 45m tall windtower that contributes to the climatic comfort of the plaza channeling down the breezes that often spire in the desert, it is important to notice that the tower is not the only element designed to improve the ambient conditions of the plaza but all the strategies are focused on the sustainability and the comfort of both the buildings and the public spaces, in this case the dense urban form is supposed to reproduce the one of the traditional local architecture and buildings façades are self shadowing reducing the reflected sun radiation in the square, streets are narrow, etc.
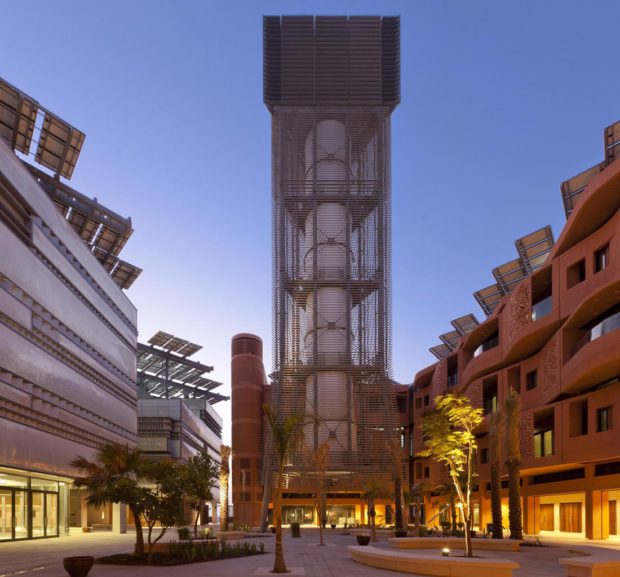

Masdar Institute Courtyard showing the wind tower. Image Copyright: Nigel Young/ Foster+Partners
This tower is a hi-tech interpretation of traditional ones, its size is greatly increased (the highest windtower in Iran is 33m high) and many design details are engineered improvements of the original windwoter concepts. The 45m teflon sleek tube is naturally designed to offer the smallest possible resistance to the passage of the wind and to reduce the possibility of condensation to the nebulized water used for passive cooling. Computer controlled louvers opens and close according the direction and the speed of the incoming wind and reduces the suction caused by negative pressure on the downwind side of the tower, with this refined mechanism, and the triangular design, the tower is always exploiting the precious wind. To increase even more the cooling potential a ring of water nozzles, also computer controlled, is placed right at the top of the shaft transforming this tower in a evaporative cooling device.
A low-tech version, though very similar in the functioning is the windtower built at the Nitzana Educational Village, in the Negev desert at the border between Israel and Egypt. This design is constituted only by a vertical metal chimney topped by a fixed wind catcher oriented towards the prevailing wind. The playful design is enhanced by a clever usage of the bottom part of the tower, a perforated ceramic brickwork is used to enclose a relatively generous meeting place that can host dozens of people from the local community, to reduce solar gain on the habitable part of the tower a sun protection is installed around it permanently shadowing the ventilating part.

Nitzana Educational Eco-Village, Nitzana. Picture courtesy of the The Jewish Agency for Israel CC BY-SA 2.0 from flickr.
The cooling process is based on a combination of wind-catching, mechanical ventilation, and evaporative cooling. In the upper part of the shaft a large fan is installed to generate an artificial windflow (power is apparently generated by solar panels placed on the south side of the tower) and under the fan two rings of nozzles are placed to implement passive evaporative cooling. Though being quite a raw design, this cooling tower uses all the technical mechanisms to achieve a cost effective cooling for the small public it has to refrigerate. Compared to the Masdar windtower this one might have a major flaw, in both the Ecobulevar and Masdar the proper cooling shaft is always protected from the direct sunlight, in this case instead the shaft is thermally conductive and prone to overheating,
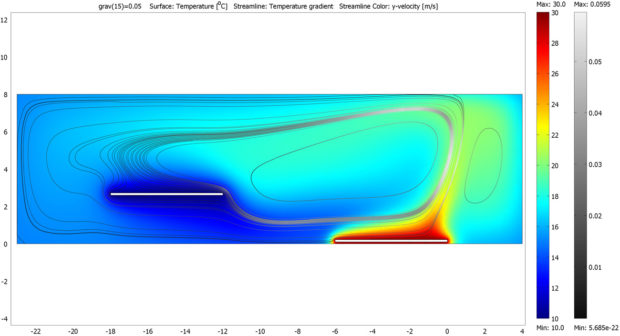
But the most advanced look at what convection means for the perception and comfort of the human body in the space has to be find in Rahm’s “Digestible Gulf Stream”. In this project, two white sleek metal boards are placed at different heights in a room, one of the boards, placed on the floor, is constantly heated to 28º C, the second one, hanging at a higher point is cooled down to 12ºC. The temperature difference between the two panels creates a convective flow, the air heated on the lower plan becomes less dense and lighter and tends to float towards the second object that gradually cools it down causing it to descend until reaching again the warm plate. This constant air flow is invisible but certainly perceivable by the human body, for the purpose of the exhibition in fact, actors with different clothing (from naked to well dressed) were standing on the plates showing various levels of comfort and doing various activities that had a different impact on the heat production.

Digestible Gulf Stream, Venice Biennale 2008 – Philippe Rahm. Image courtesy of Philippe Rahm.
Rahm’s pioneering work in “climatic architecture” is extremely interesting, in this case the space is defined only by its temperature which is something we are not really used to, our normal physical division of space (walls, windows, curtains…) is totally visual but then our comfort is determined by variables like air temperature, this is particularly true in public space, where usually there are no “rooms” and the use (or the avoidance) of space is more often determined by factors like shadow, noise, comfort, etc.